ECVET - Application to mobility projects
Main menu:
- Home Page
- ECVET - Overview
- ECVET - Key topics
- Sesamo and ECVET
- User guide
- Coordinator - Supervisor guide
System
ECVET - Key topics > More about VET > Estonia
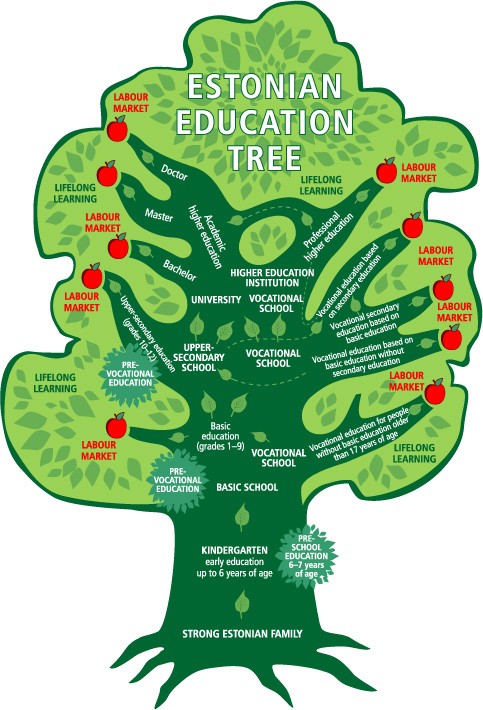
The primary education is divided into 9 levels; 7 levels are common. The last two levels are different since they enable also to get a pre-vocational training.
For persons without basic education and having passed the minimum school-leaving age (17 years) it is possible to continue their education in vocational schools. If you have basic education, so you can choose among four possibilities to continue your studies. The same path can be followed in the secondary education.
The principles of the VET system were established in the Education Act and the Vocational Education Act (1998) which sets out the types of vocational training, the activities, the management and funding of VET providers and deals with the internal assessment and supervision. The requirements for the vocational training, the curricula and the Vocational Education Standard have been established with a governmental act.
VET is funded by the Ministry of Education and Research according to public allocations.
A person can access the vocational training if he/she has a basic education or if he/she is 17 years old and without a basic education. Vocational courses deal with general subjects concerning a profession and the on- the- job training.
The vocational qualifications system is based on professional standards functional to define the curricula in the high and vocational education.